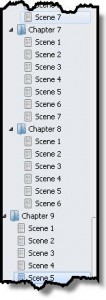
Okay, this post will make Patrick Hester very happy. Why? Patrick loves Scrivener. He might as well be a spokesperson, seriously! But for writers, this post should also make you happy, especially if you’re a pantser like me. In case anyone doesn’t know the terms, pantsers are those of us who, rather than outlining, prefer to discover the story as we write. We may make a few notes about plot twists, characters, scenes, etc., but mostly we write unstructured. It allows us to experience the story in the same way a reader or POV character might. For strict outliners, it sounds like craziness, living on the edge. Might as well jump off a cliff. But for pantsers, it’s liberating.
Okay, this post will make Patrick Hester very happy. Why? Patrick loves Scrivener. He might as well be a spokesperson, seriously! But for writers, this post should also make you happy, especially if you’re a pantser like me. In case anyone doesn’t know the terms, pantsers are those of us who, rather than outlining, prefer to discover the story as we write. We may make a few notes about plot twists, characters, scenes, etc., but mostly we write unstructured. It allows us to experience the story in the same way a reader or POV character might. For strict outliners, it sounds like craziness, living on the edge. Might as well jump off a cliff. But for pantsers, it’s liberating.

Regardless, Literature and Latte’s Scrivener is certainly a popular writing program. It’s also a lot more affordable than most these days. Developed by writers, for writers, it used to be available only for MAC but now there’s a PC version as well. And priced at just $40 US for the full version, it’s a bargain. What is Scrivener?
Scrivener is a word processing program designed specifically for writing prose. You create folders and text pages within them, allowing each chapter and scene to be separate. Or, you can just create one big folder and write it all there. Since the program was designed to be used breaking things up, that’s the method I’d recommend, but I don’t want to scare off those who bristle at the idea. Why do I recommend that? What are its advantages?
Well, the advantages of it are some of the very things that make Scrivener advantageous for pantsers.
1) You can move scenes within and outside of chapters with just a mouse click and drag. Ever write something and realize it’s in the wrong place? Every write something and decide later it doesn’t quite work but feel loathe to throw it out? No more creating new holding documents or saving scenes to clog up your folders. Instead, you can move it around. Switch the order of scenes within a chapter. Move a scene to another chapter. Move a scene to a holding folder for use later when relevant. All can be done in a matter of seconds with Scrivener. Use either the menu bar to the left edge of the screen and drag and drop or use the corkboard and just click and drag things around.
2) Formatting is a snap. You just type your words and let Scrivener do the rest. It can even convert italics to underlining, emdashes to double dashes, and more. It adds headers, page numbers, chapter headings, all fairly seemlessly, saving you a lot of work. And with the templates included you can format it not just standard manuscript format but as paperbacks and other options, even save to PDF.
3) Exporting To Word is easy. .RTF or .DOC export is simple. I use it daily to back up my work, but, technically, you don’t have to export until you’re done and ready to send it off. Use those handy formatting features I just mentioned to format the document per guidelines of a specific editor, agent or market. Conversion is fast and you can then make any adjustments to the Word document that are necessary (usually only a few). Once you learn how to use it, the adjusting will not be very involved. You can also set up a title page including word count (which the program counts automatically), your contact info and agent, etc.
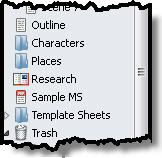 4) Notes Within The Project. You can keep notes within the project itself. Scrivener’s default projects include folders for character notes, place notes, and research in addition to your manuscript. And the trash saves anything you drag and drop there until you tell it to delete. All stored in a project folder that’s easy to back up. And none of the extra stuff converts to word unless you tell it to.
4) Notes Within The Project. You can keep notes within the project itself. Scrivener’s default projects include folders for character notes, place notes, and research in addition to your manuscript. And the trash saves anything you drag and drop there until you tell it to delete. All stored in a project folder that’s easy to back up. And none of the extra stuff converts to word unless you tell it to.
5) Synopsis & Outlining Ease. Using the synopsis and outline features, Scrivener can save a tone of time. Wait! We’re pantsers! Yeah, I know, but if you sell that manuscript or get an agent, you’re going to need a synopsis and probably an outline. Editors often ask for these, especially for second books. These resources allow you to more easily cull data from your project into outlines and synopses in a much more rapid fashion. I don’t know about you, but anything that makes those things easier for me is awesome in my book.
6) Finding scenes or chapters for review is a snap. Need to reference a previous scene? Just scan the corkboard or left side menu, click and you’re there, boom! And you can go back to the scene you’re working on just as fast. No need to use Find searches for a phrase or flip back and forth or print one so you can have it handy. No need even for two monitors so both can be open or a split screen. Scrivener makes that easy.
Here’s another advantage. Literature and Latte is so confident in their project, they let you download a full version for a one month trial FREE. Yep. Try it out first. If you don’t like it, convert the project into Word and you can continue working there. It’s really a great way to try out something new. And they know that if you take the time to learn and use it effectively, you’ll probably wind up just buying it and continuing to use it. I know I did.
Believe, I know how hard it can be to change, how set we writers get in our routines i.e. what works for us. I also know how little time we have or want to spend learning new software or changing all that, but what if it could save you time and frustration in the long run, leaving you more time to write?
Whatever the case, I find Scrivener to be incredible freeing in a number of ways. All of the above have saved me time and stress. And as the program continues to improve and I continue to explore it, I’m sure it will only get better. Others of you who use Scrivener, what are advantages you’ve found? I’d love to hear them in comments. For what it’s worth…
For downloads, demos and more information, check out the Scrivener website here: http://www.literatureandlatte.com/scrivener.php
 Bryan Thomas Schmidt is an author and editor of adult and children’s speculative fiction. His debut novel, The Worker Prince(2011) received Honorable Mention on Barnes & Noble Book Club’s Year’s Best Science Fiction Releases for 2011. A sequel The Returning followed in 2012 and The Exodus will appear in 2013, completing the space opera Saga Of Davi Rhii. His first children’s books, 102 More Hilarious Dinosaur Books For Kids (ebook only) and Abraham Lincoln: Dinosaur Hunter- Land Of Legends (forthcoming) appeared from Delabarre Publishing in 2012. His short stories have appeared in magazines, anthologies and online. He edited the anthology Space Battles: Full Throttle Space Tales #6 (2012) and is working on Beyond The Sun for Fairwood Press, headlined by Robert Silverberg, Kristine Kathryn Rusch, Mike Resnick and Nancy Kress, a Ray Gun Revival Best Of Collection for Every Day Publishing and World Encounters and Space & Shadows: SpecNoir with coeditor John Helfers, all forthcoming. He hosts #sffwrtcht (Science Fiction & Fantasy Writer’s Chat) Wednesdays at 9 pm ET on Twitter and is an affiliate member of the SFWA.
Bryan Thomas Schmidt is an author and editor of adult and children’s speculative fiction. His debut novel, The Worker Prince(2011) received Honorable Mention on Barnes & Noble Book Club’s Year’s Best Science Fiction Releases for 2011. A sequel The Returning followed in 2012 and The Exodus will appear in 2013, completing the space opera Saga Of Davi Rhii. His first children’s books, 102 More Hilarious Dinosaur Books For Kids (ebook only) and Abraham Lincoln: Dinosaur Hunter- Land Of Legends (forthcoming) appeared from Delabarre Publishing in 2012. His short stories have appeared in magazines, anthologies and online. He edited the anthology Space Battles: Full Throttle Space Tales #6 (2012) and is working on Beyond The Sun for Fairwood Press, headlined by Robert Silverberg, Kristine Kathryn Rusch, Mike Resnick and Nancy Kress, a Ray Gun Revival Best Of Collection for Every Day Publishing and World Encounters and Space & Shadows: SpecNoir with coeditor John Helfers, all forthcoming. He hosts #sffwrtcht (Science Fiction & Fantasy Writer’s Chat) Wednesdays at 9 pm ET on Twitter and is an affiliate member of the SFWA.