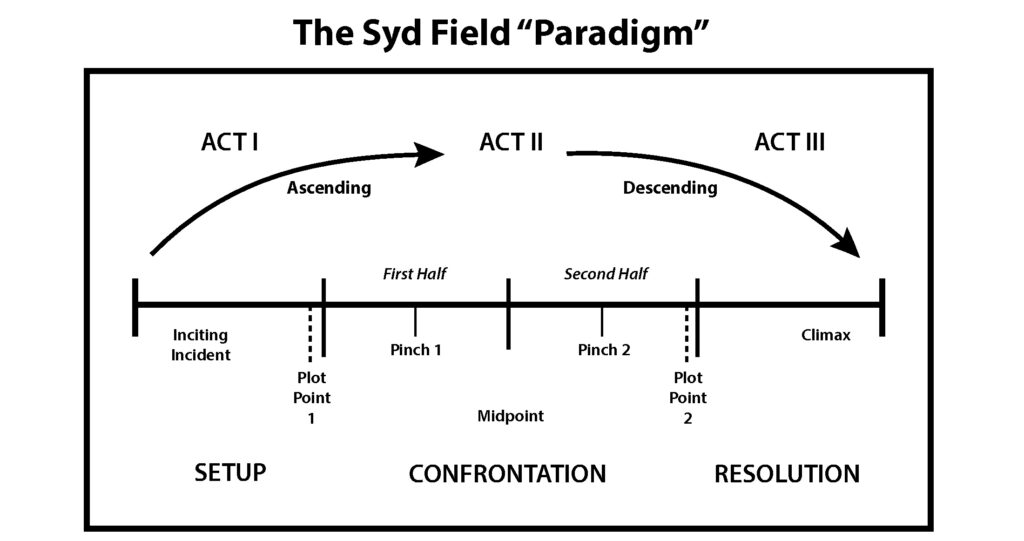
The following is an excerpt from my book How To Write A Novel: The Fundamentals of Fiction, Chapter 8:
The following is an excerpt from my book How To Write A Novel: The Fundamentals of Fiction, Chapter 8:
Pacing
When people hear the word pacing, they typically think of “slow” or “fast,” or perhaps “action,” but in novels pacing needs both to be successful. Dictionary.com defines pace as:
- a rate of movement, especially in stepping, walking, etc.;
- a rate of activity, progress, growth, performance, etc.; tempo.
In regards to your novel, the pacing is a combination of steady, fast, and slow passages creating a rhythm that flows for readers, engaging and holding their interest, while still pausing to let them catch their breath and regroup from time to time.
Experienced novelists tend to get a natural sense of pacing as they write. Newer writers, however, will have to learn this. Imagine yourself on a treadmill, speed slowly increasing. Your pulse begins pounding, your breathing increases, the rhythm of the humming tread and your footfalls accelerating to combine into a steady beat. Then imagine keeping that speed for ten hours straight. Do you think you’d last? Probably not. The same is true of readers reading a novel.
While it is true that readers like stories where “something happens,” and action is a big part of that, readers also need stories that stop for reflective moments, too, allowing them to catch their breath, take a sip of water, grab a snack, and regroup. In constructing your plot, you should learn to plan for such a rhythm. Two or three high points of tense, fast pace, should be followed by a slower, thoughtful point before the next two or three fast, tense points begin. There are various ways to accomplish this which we will look at next.
Since action is the driving force of drama, let’s start with action. But don’t worry, we’ll get to how to slow it down too, right after. Just like I said we should.
Writing Action
I don’t know about you, but I’ve always been a fan of action. Movies like the Lethal Weapon and Die Hard series always entertained me. I like action in my reading, too. Space opera is my favorite science fiction genre and sword & sorcery tops my fantasy favorites, but I also spend a great deal of my time reading thrillers and police procedurals. Is it any wonder that I find myself often writing action in my stories?
One of the best action writers I know is Jonathan Maberry, the New York Times bestselling author of the Joe Ledger thrillers and several other series. Let’s look at an action scene from one of his novels, Assassin’s Code:
I struggled to get to my feet. A minute ago I had thought that the whole world was sliding into the mouth of hell, but now a different kind of hell had come to this place of shadows. There were screams and Upierczi running everywhere. Flares popped in the air, painting everything in bright white light. I took a step toward Grigor and my foot kicked something. I looked down and saw the code scrambler. I bent and picked it up. “Cowboy—on your six!” It was Khalid’s voice, and I turned to see one of the vampires four feet away. I had no time to run. I didn’t want to run. As he slammed into me I buried the pistol under his chin and blew off the top of his head. We hit the ground and I lay there, Upierczi blood all over me. In my face, my eyes, my mouth. I rolled over and threw up. Grigor was still screaming. Then I heard a sharp yelp of pain and looked up to see the Upierczi fling Ghost aside. Ghost hit the side of a packing crate and col- lapsed, spitting blood onto the floor. I saw a couple of teeth, too. That made me mad. Maybe I needed that to shake off the damage and the pain. I came out of my daze and finally the situation gelled in my mind. The Upierczi were rushing outward from me, some were seeking cover, most were rushing at Echo Team. Bunny and Top were at the foot of the metal stairs. Bunny had a combat shotgun with a drum magazine and he was firing, firing, firing. Everything that came at him died. The heavy buckshot soaked with garlic oil poisoned every Upier that wasn’t instantly killed by his blasts. The ones who took a few pellets staggered away, gagging and twitching with the onset of allergic shock. Top was watching his back, firing a big Navy Colt automatic, the hollow points doing terrible work in the tightly packed crowd. On the other side of the chamber, Khalid and Lydia were behind a packing crate, using it as a shooting blind to create a cross fire. “Frag out!” Lydia yelled and lobbed grenades into the heart of the vampires. The fragmentation grenades weren’t filled with garlic, but the blasts tore the monsters to pieces. I saw three Upierczi running along the wall toward them, well out of Lydia’s line of sight. I raised my pistol but before I could fire the monsters went down, one, two, three, their heads burst apart by sniper rounds. John Smith, firing from somewhere I couldn’t see. My knife was on the floor too, and I grabbed it as well. I shoved knife and scrambler into my pocket and tapped my earbud. “Echo, Echo, this is Cowboy. I have the football and I need a doorway out of here.” “I have your back,” came the reply, but it wasn’t in my earbud. I whirled, and there she was. Dressed all in black, splashed with blood, a wickedly curved blade in each hand. “Violin,” I began, but she shook her head. “No time.” She lunged past me as several Upierczi rushed my blind side. Until that moment I didn’t understand what “gifts” the dhampyri had gotten from the cauldron of their birth. Violin was not as physically powerful, but my God, she was fast. She met the rushing vampires, and even though I am trained to observe and understand combat at any level, I could not follow what happened. Her arms moved so fast, her body spun and danced as she threaded her way through the pack, the silver blades whipped with such frenzy that the monsters seemed to disintegrate around her. It was so fast that their blood hung in the air like mist. It was hypnotic and beautiful in the most awful way that perfect violence can be beautiful; and it was horrible because there was nothing natural about what I was seeing. Violin was a thing born from rape, torn from a tortur-ed mother by a monster of a father, raised in a cu— ture of rage and humiliation. If it was possible for the concept of vengeance to be embodied in one form, then that’s what I was seeing. The Upierczi did not understand the nature of their death. I could see that on their faces. They saw a woman— something that to them represented a thing to be taken and used and discarded— and they attacked her with the arrogance of habitual users. They expected her to fall. They expected her to be weak. They did not expect the precise and unstoppable fury of this daughter of Lilith. She killed and killed and killed. And yet, with all of that, I knew it wasn’t going to be enough. There were at least a hundred of the Upier-czi in the chamber. More of them were seeded through the staff of the refinery. There were a handful of us. We were going to lose this fight. In my earbud I heard John Smith say, “Mother of God.” And then I heard him scream. I wrenched myself away from Violin and raised my gun, searching the catwalks for Smith. I saw him. I saw what was left of him fall. Grigor, bloody, torn, perhaps dying, stood on the cat-walk fifty yards away. His mouth was bright with fresh blood. John Smith struck the hard stone floor in a broken sprawl. His throat was completely torn away. “No!” I heard that scream of denial fill the air. From Bunny’s throat, from Lydia’s and Khalid’s. From my own. Before I knew what I was doing I was running with my gun held in both hands, firing, firing. Bullets pinge and whanged off the steel pipes of the catwalk, but Grigor ducked away and fled out through an open doorway. I raced toward the stairway, but Khalid was closer and he bolted up the metal steps in hot pursuit. Seven Upierczi saw what was happening and they leapt like apes onto the pipes and climbed upward. I emptied my magazine at them. One fell away. By the time I reached the foot of the stairs I had th magazines swapped out and I ran upward. I was still hurt, still bleeding. Maybe inside, too. My chest was a furnace and it felt like it was consuming me, but I didn’t care. As I reached the top deck, the last of the Upierczi turned and blocked my way. I put three rounds through his face and kicked his body out of my way. Behind me there was another massive explosion, and I lingered at the doorway, knowing that the blast signature didn’t match our fragmentation grenades. I was right. Smoke and fire billowed out of one of the tunnels and Upierczi bodies were flung backward. Then a wave of new figures flooded in. Thirty of them. Women. Arklight. The Mothers of the Fallen come for justice of a kind. The battle below became a bloodbath. I turned away and ran after Khalid, the Upierczi, and Grigor.
Note the short sentences and paragraphs, as well as short spurts of dialogue. The description, action, and dialogue are all short and spaced so that readers’ eyes will flow down the page at a quick pace as they take it in. Also, note the lack of exposition or great detail. This is not the time for it. As a trained martial artist and experienced bodyguard, Maberry has an innate sense of how action really works and makes his fight scenes as realistic as possible. For those of us lacking such background, writing action scenes can be a challenge. In movies, you have visual and other clues to use to inspire the tension and pacing in the audience, but when writing prose, this can be more difficult. So here are a few key tips I’ve learned:
 1) Write in short snippets as much as possible. Action scenes are not the time for long internal dialogues by characters. Think about a time you were involved in a high adrenaline situation. You didn’t have time to take long pauses for deep thinking. You had to react and do so quickly and so must your characters. The same is true of long speeches. People tend to be interrupted in speaking by the need to act or react. So dialogue and even action should be described in short spurts. If you have more than four sentences to it, think twice about whether it should be split up.
1) Write in short snippets as much as possible. Action scenes are not the time for long internal dialogues by characters. Think about a time you were involved in a high adrenaline situation. You didn’t have time to take long pauses for deep thinking. You had to react and do so quickly and so must your characters. The same is true of long speeches. People tend to be interrupted in speaking by the need to act or react. So dialogue and even action should be described in short spurts. If you have more than four sentences to it, think twice about whether it should be split up.
2) Use action to break up dialogue and dialogue to break up action. Intersperse the two components in short segments to add a sense of pacing and tension. Writing long sections of dialogue and long sections of action will tend to read slow and thus stall the pacing. This is especially true of dialogue as noted above. Alternating them adds a sense of realism and keeps things moving.
3) Get to the point. Long descriptions of weapons and scenery don’t belong here. If things need to be set up, do it before the sequence occurs so you don’t have to interrupt the action to do it. You want to focus on sensory details–what the characters see, feel, touch, etc. Are they sweating? Are they hurting? Not on what the building behind them looks like or even the street itself. You don’t want to spend pages like Tom Clancy describing their weapon here. We need to know what it is and how it works and their skill level so we cannot be surprised by their actions, but set that up elsewhere. During the action, we should already know.
4) Don’t make it too easy. Yes, the hero will likely win. But make it a challenge. Be sure and make the opponents threatening enough that the hero is in real jeopardy, otherwise the dramatic impact will be greatly lessened. No matter how skilled your hero is, he or she must have to face obstacles. In action sequences the odds should seem stacked against him. Let them bleed from a wound. Let them misfire or miss with the sword. Let them sweat and even have to run, barely escaping. Sometimes it’s even good to let them lose one time only to have them win later on. Force them to stretch themselves in some way to succeed. Make them human or the reader’s will struggle to care.
5) Keep it believable. This goes hand in hand with number 4. Real people are imperfect. They make mistakes. They fail. Make sure your action sequences are well researched and realistic. Besides humanizing the hero, don’t have vehicles or weapons performing beyond their capabilities. You may assume readers won’t know the difference but some will. And writing without limits rings hollow. Make sure you respect the limits and use them to up the tension. A man stuck with a sword fighting men with guns will face tense moments. A man against incredible odds is a man we root for.
6) Keep it tight. Anything absolutely not necessary should be cut. This includes long descriptions and dialogue as mentioned in number 1 but also the scene openings and closings. The rule I learned in film school was to get in a scene as late as possible and out as soon as possible. Nothing hurts pacing more than disobeying this rule. Be sure you start the action as fast as possible and end it the same. Don’t drag it out unnecessarily in your desire to make it more dramatic or a “cooler” sequence. Make it exactly as long as it really needs to be to serve the story and no longer.
7) Give the readers breathing space. Be careful about putting too many action sequences too close together. Movies build to a climax which may have twenty minutes of action but before that action scenes are interspersed with slower moments. Make sure you intersperse your action sequences with moments of character building and reflection, dialogue and discovery–slower sequences which allow readers to breathe a bit before the next intense action scene. In between scenes are where you make action sequences matter. Action is not just about a character we care about surviving but about stakes he or she has in that victory. What is the character’s driving need or goal? This gets set up in other scenes and provided driving undercurrent to the action which makes us care.
8 ) Pick your moments. Action stories tend to have several sequences spread throughout. Be sure you consider in choosing which sequence to include where the overall dramatic level of them. You want the biggest action sequence in the entire piece to be either at the closing of the piece. Those in between should leave room for a build up to the major action sequence to come. Ideally, each scene builds up to those that follow but this can be accomplished in ways besides upping the stakes and tension or odds. With proper character arcs, character’s emotional stakes can be developed in such a way that each later sequence matters that much more, making the readers care more as well.
9) Make it matter. Action scenes do not exist solely to entertain readers and add tension. They have a greater purpose to serve the story. Something must happen which ups the stakes or increases the challenges with each scene in your story and action scenes are no exception. Don’t write action for the sake of action. Write action because it serves the story. Every action sequence should move the story and characters forward in their journey, if not, they don’t belong in the story.
10) Incorporate humor. Humor is a great tool for not only breaking the tension but building character during action sequences. It’s no accident characters like Lethal Weapon’s Riggs and Die Hard’s McClane engage in witty banter during such moments and your characters can as well. From funny actions to funny dialogue snippets, this makes the action both more enjoyable and less tense when done at the right moments and can add a lot to reader enjoyment. Don’t be afraid to incorporate it when you can. It doesn’t have to be cheesy catch phrases either. It’s all in the wording.
Now, thinking about these tips, go back and read the Maberry passage again and see how they are applied. He uses every technique mentioned in his action scenes, and in between, he gives us breathing space. So what are some techniques for doing that?